Data Integrity
Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) is the codification of the general and permanent rules and regulators published in the Federal Register. These rules are published by Executive Departments of the Federal Government of the United States.
- Part 11 is the part of Title 21 of CFR that establishes the US FDA regulations on Electronic Records and Electronic Signatures (ERES).
- Part 11, defines the criteria under which ERES are considered trustworthy, reliable and equivalent to paper records.
Part 11 applies to records in electronic form that are created, 26 modified, maintained, archived, retrieved, or transmitted under any records requirements set 27 forth in Agency regulations.
What is data?
Information derived or obtained from raw data.
What is Data Integrity?
Data integrity refers to the completeness, consistency, and accuracy of data. Complete, consistent, and accurate data should be attributable, legible, contemporaneously recorded, original or a true copy, and accurate (ALCOA)

Data
Data can be ‘ electronic’ or ‘ Paper based ’ or ‘Hybrid ‘

Data lifecycle:
From initial data generation and recording through processing (including transformation or migration), use, retention, archiving, retrieval and Destruction.
Why Data Integrity ?
- Assures the Quality, Safety and efficacy of the Drug
- The documented data is the only record of the activity presenting the quality of the product
- Reliability and trustworthy records
- Questioning Data Integrity = Loss of Trust
- Submitting false data to FDA is a Criminal violation under FD & C Act
- Data Integrity is mandated by World Health Organization, FDA, MHRA, ICH, Council of Europe
What is“metadata”?
Metadata is the contextual information required to understand data. A data value is by itself meaningless without additional information about the data. Metadata is often described as data about data. Metadata is structured information that 80 describes, explains, or otherwise makes it easier to retrieve, use, or manage data.
What is an “audit trail”?
For purposes of this guidance, audit trail means a secure, computer-generated, 95 time-stamped electronic record that allows for reconstruction of the course of 96 events relating to the creation, modification, or deletion of an electronic record. 97 An audit trail is a chronology of the “who, what, when, and why” of a record. For 98 example, the audit trail for a high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) 99 run could include the user name, date/time of the run, the integration parameters 100 used, and details of a reprocessing, if any, including change justification for the reprocessing.
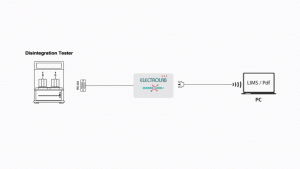
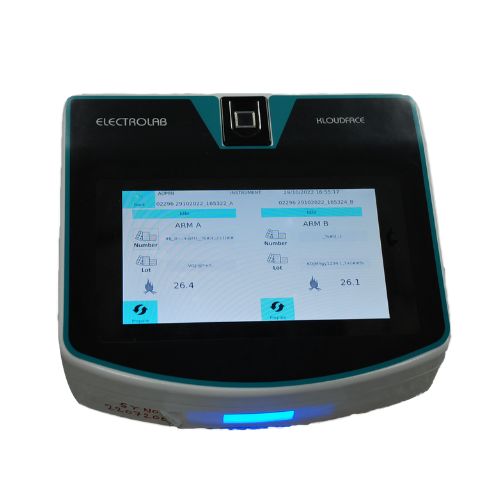
Kloudface device is one stop solution for your legacy instruments. Kloudface is powered by Integros 2.0 Operating system. Kloudface Gen2 is 7 inch touch screen interface which is connected to your legacy instrument through serial port and keeps data in compliance environment to meet all data integrity guidelines with traceability and logbook.

Data Integrity Issues
- Backdating/ Postdating / Missing Signature
- Fabricating / Faking data
- Copying existing data as new data
- Releasing failing data
- Hiding / obscuring SOP or Protocol Deviations
- Not saving electronic or hard copy data
- Use of non- validated software
- Mismatch between reported data and actual data
- No Links/ traceability to source documents or original data
- Re- running samples/ test until release / No inappropriate Audit trial
- Discarding deleting of data / omitting negative data ( Like OOS)
- Disabling audit trials in electronic data capture system
- Fabricating training data
- Having unofficial batch sheets and Analytical reports
Solving Data Integrity issues can include
- limiting system access to authorized individuals
- use of operational system checks
- use of authority checks
- use of device checks
- determination that persons who develop, maintain, or use electronic systems have the education, training, and experience to perform their assigned tasks
- establishment of and adherence to written policies that hold individuals accountable for actions initiated under their electronic signatures
- appropriate controls over systems documentation






0 Comments